Part 1: Contested Foundations of Archaeology Related Posts: Part 2: Archaeological Evidence – A Reality Check Part 3: Biblical History and Textual Interpretation One of my readers suggests I have been too simplistic when I dismissed the Documentary Hypothesis and questioned the validity of historical criticism. After all, rational discourse demands interrogation of texts. He … Continue reading “Historical Criticism and Textual Interpretation – Part 1/3.”
Part 1: Contested Foundations of Archaeology
Related Posts:
Part 2: Archaeological Evidence – A Reality Check
Part 3: Biblical History and Textual Interpretation
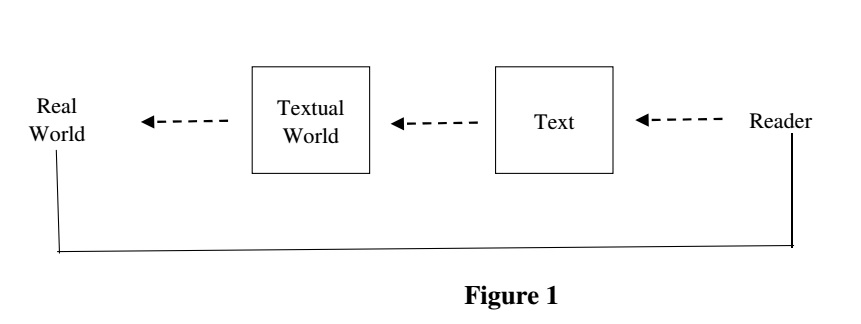
One of my readers suggests I have been too simplistic when I dismissed the Documentary Hypothesis and questioned the validity of historical criticism. After all, rational discourse demands interrogation of texts. He submits that my rejection of historical criticism is erroneous as Christianity is a faith grounded in the “God Who Acts in history”. Worse still, insulating the Bible from rational historical criticism amounts to adopting a dogmatic mindset that is no different from that of the Islamists.
It is true that I reject the Documentary Hypothesis for literary and historical reasons. However, my assessment of historical criticism is more nuanced. Unlike the Islamists and other extreme fundamentalists, I make careful use of the historical method. To be sure, there is historical method and there is historical method. The historical method that I reject is that based on the Enlightenment rationality championed by Ernst Troeltsch who taught that history is a closed continuum that precludes reference to divine revelation. Human reason becomes sovereign in historical judgment with pretensions of neutrality in interpretation. Not surprisingly, critical scholars who elevate human reason above divine revelation display skepticism towards the reliability of biblical history and its truth claims. However, their claim of neutrality has been debunked by the hermeneutical critique of Hans-Georg Gadamer and Paul Ricoeur.
My presuppositions for relating history and the biblical texts is one of believing criticism and post-critical hermeneutics. I seek to apply a historical method that is consistent with belief in God’s manifestation of himself through mighty acts, prophetic interpretation of the vicissitudes of the history of biblical Israel, and the final inscription of God’s Word in the Bible. Such a belief is rejected by critical scholars who then deploy a critical historical method that takes liberty with the biblical text which they do not regarded as inspired or authoritative. Continue reading “Historical Criticism and Textual Interpretation – Part 1/3.”