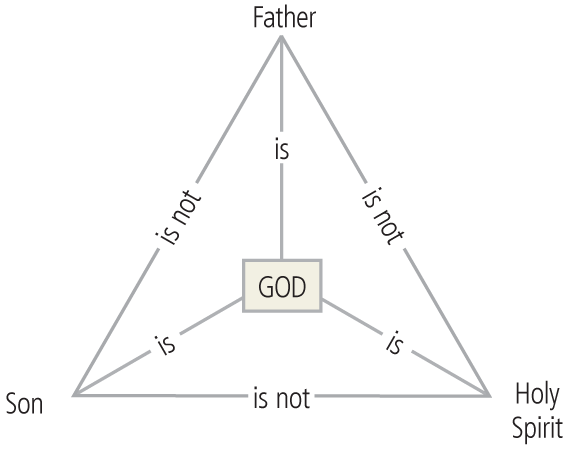
Open theism is the belief that God is not timelessly eternal. “God changes in some ways so as to respond appropriately to a changing creation…God’s foreknowledge is limited, because of the limitations he has placed upon himself in giving humans freewill.” /1/ The idea that God has limited foreknowledge was first formulated by the Polish Socinian movement in the late 16th century. It was recently revived by several Open Theists (Clark Pinnock, Richard Rice & John Sanders et al) when they jointly published the seminal work, The Openness of God (IVP, 1994). However, anyone who feels swayed by their sophisticated arguments should recall the old-time rebuttal, “Your argument is logical but your conclusion is unfounded because your premises are wrong.” Applying logic to wrong premises only leads to conclusions that do not correspond to reality. For the same reason, the logic of Open Theism results in a god who is in conflict with the God of Biblical-Classical theism because its premises or fundamental philosophical intuitions are questionable. Continue reading “The Limited god of Open Theism is Not the Almighty God of the Bible”

 THIRTEENTH QUESTION: MIDDLE KNOWLEDGE
THIRTEENTH QUESTION: MIDDLE KNOWLEDGE It has been suggested by some bloggers that exegesis is on the side of the Calvinists while logic is on the side of the Arminians. This suggestion sounds plausible since the majority of Christian philosophers today are either Arminians or Open theists. The bloggers are correct in acknowledging that Calvinists offer robust exegesis to support their arguments which is evident in the works of Thomas Schreiner, John Piper, Sam Storms and James White. However, the suggestion is mystifying since historically Calvinists have been accused of imposing of a rigid logical system onto Scripture. We can only conclude that the bloggers who suggest that Calvinists lack rigor in logical analysis have never bothered to read Calvin and his successors like Francis Turretin, John Owen, Jonathan Edwards or Dutch Reformed theologians like Wilhelmus Brakel and Petrus van Mastricht. A quick glance of Richard Muller’s 4-vol (2176 pages) work on Post-Reformation Reformed Dogmatics should immediately impress the reader of both the acuity and logical brilliance displayed by the Calvinists. It was precisely because the doctrinal disputations of the Reformed Scholastics were dominated by austere logic, where conciseness and clarity trumps readability that Calvinism has been accused on putting logic above Scripture.
It has been suggested by some bloggers that exegesis is on the side of the Calvinists while logic is on the side of the Arminians. This suggestion sounds plausible since the majority of Christian philosophers today are either Arminians or Open theists. The bloggers are correct in acknowledging that Calvinists offer robust exegesis to support their arguments which is evident in the works of Thomas Schreiner, John Piper, Sam Storms and James White. However, the suggestion is mystifying since historically Calvinists have been accused of imposing of a rigid logical system onto Scripture. We can only conclude that the bloggers who suggest that Calvinists lack rigor in logical analysis have never bothered to read Calvin and his successors like Francis Turretin, John Owen, Jonathan Edwards or Dutch Reformed theologians like Wilhelmus Brakel and Petrus van Mastricht. A quick glance of Richard Muller’s 4-vol (2176 pages) work on Post-Reformation Reformed Dogmatics should immediately impress the reader of both the acuity and logical brilliance displayed by the Calvinists. It was precisely because the doctrinal disputations of the Reformed Scholastics were dominated by austere logic, where conciseness and clarity trumps readability that Calvinism has been accused on putting logic above Scripture.