
Kairos Podcast 6: Early Trinitarianism from NT to Nicaea. Part 6/6
LINK: The Creedal Imperative and Trinitarian Confession of Christian Faith and Theology
Recapitulation – how the doctrine of Trinity unfolded as the early church countered heresies.
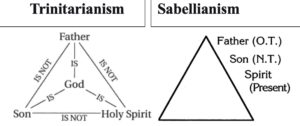
Tertullian defined the Trinity as three persons in one essence, thus highlighting the foundational biblical teaching on the oneness of God and the three distinct yet equal persons of the Father, Son, and Holy Spirit. The Council of Nicaea, with Athanasius, applied the term “essence” (ousia) to the person of Christ. Christ is of the same essence (homoousios) with the Father. Yet Christ also exists as a separate person, distinct in his own identity as Christ the Son. In short, biblical-Nicene trinitarianism succinctly insists that Christ is truly God and anyone who teaches otherwise is teaching heresy.
The Creedal Imperative – Biblicism insists that one only needs the bible to formulate Christian belief by relying on rigid proof-texting of selective bible verses at the expense of context and other biblical teachings. In contrast, the historic church affirms that creeds (like the Nicene Creed) are essential as they assist the church in understanding Scripture, provide succinct and normative summary of the foundations of the Christian faith (rule of faith) and protect believers from false doctrines.
You may view the video at
The Creedal Imperative and Trinitarian Confession of Christian Faith and Theology

 The standard translation takes Gen.1:1 to be an independent clause which refers to the absolute beginning of the universe: “In the beginning God created the heavens and the earth.” The word bərēʾšît (beginning) denotes the start of a whole sequence of events, that is, the absolute beginning of “the heavens and the earth.” The phrase is a rhetorical device (merism) which combines two extremes in order to refer to everything in between them. The translation is consistent with the idea that God created the whole universe ex nihilo.
The standard translation takes Gen.1:1 to be an independent clause which refers to the absolute beginning of the universe: “In the beginning God created the heavens and the earth.” The word bərēʾšît (beginning) denotes the start of a whole sequence of events, that is, the absolute beginning of “the heavens and the earth.” The phrase is a rhetorical device (merism) which combines two extremes in order to refer to everything in between them. The translation is consistent with the idea that God created the whole universe ex nihilo.


 Many critical scholars in Western universities suggest that the biblical Creation and Flood stories borrowed ideas from Ancient Near Eastern Texts (ANET). For example, the Creation story in Genesis must be influenced by the Babylonian creation story of Enuma Elish since the story in Genesis is briefer and the preserved records of Genesis belong to a later date. However, Kenneth Kitchen rejects this notion. He writes, “The common assumption that the Hebrew account is simply a purged and simplified version of the Babylonian legend (applied also to the Flood stories) is fallacious on methodological grounds. In the Ancient Near East, the rule is that simple accounts or traditions may give rise (by accretion and embellishment) to elaborate legends, but not vice versa. In the Ancient Orient, legends were not simplified or turned into pseudo-history (historicized) as has been assumed for early Genesis.”/1/
Many critical scholars in Western universities suggest that the biblical Creation and Flood stories borrowed ideas from Ancient Near Eastern Texts (ANET). For example, the Creation story in Genesis must be influenced by the Babylonian creation story of Enuma Elish since the story in Genesis is briefer and the preserved records of Genesis belong to a later date. However, Kenneth Kitchen rejects this notion. He writes, “The common assumption that the Hebrew account is simply a purged and simplified version of the Babylonian legend (applied also to the Flood stories) is fallacious on methodological grounds. In the Ancient Near East, the rule is that simple accounts or traditions may give rise (by accretion and embellishment) to elaborate legends, but not vice versa. In the Ancient Orient, legends were not simplified or turned into pseudo-history (historicized) as has been assumed for early Genesis.”/1/ Kairos Podcast 6: Early Heresies Part 2/6
Kairos Podcast 6: Early Heresies Part 2/6