Herman Bavinck’s Metaphysics of Knowledge. BB002
Knowledge beyond the Immanuel Kant’s Bounds of Pure Reason
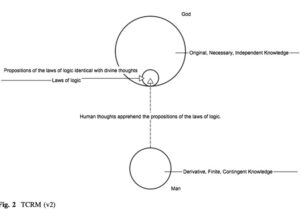
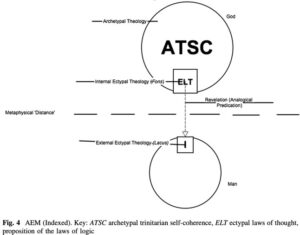
“Pure reason” refers to Immanuel Kant’s idea of the faculty of reason operating independently and applying a priori concepts or innate forms and categories of thought to impose order to makes sense of sensations received from the world. Effectively, the mind becomes the measure and bounds of all knowledge. But we can never be sure if there is correspondence between the structured experience in mind and reality outside the mind. Kant’s conclusion is that there is an unbridgeable gap between what the mind perceives with its constructed concepts and representations (phenomena) and the world or the things-in-themselves (noumena).
Herman Bavinck agrees with Kant that the mind plays a determinative role for all meaningful experience but Bavinck argues that Kant’s epistemological dualism undermines knowledge altogether. “For, says idealism [Kant], if a thing and the representation of a thing are two different realities, then we must despair of knowledge of the thing. Since we simply can never test our representation of a thing by the thing itself, we can never step outside of ourselves, of our representational world…We always remain inside the circle of our representations and never come into contact with the thing itself, only with our representation of the thing. Stated differently, only that which is conscious exists for us; I can only think the thought, not the thing itself. That which is not my thought is inconceivable, unknowable to me; it does not exist for me.” [RD 1.216] Continue reading “Herman Bavinck’s Metaphysics of Knowledge. BB002”