 A. Definitions
A. Definitions
1) Determinism: Determination is, intuitively, the thesis that, given the past and the laws of nature, there is only one possible future. [Van Inwagen, Essay on Free Will (Oxford UP, 1983), p. 65] In theological terms, an event (such as choice or action), is determined, that is, it must occur because there are sufficient conditions for its occurrence obtained earlier by the decrees of God.
The two major contending positions in the debate on determinism and free will are:
Compatibilism is the idea that there is no conflict between determinism and free will.
Incompatibilism is the idea that determinism rules out free will.
2) The principle of alternative possibilities (PAP)
PAP: A person is morally responsible for what he has done only if he could have done otherwise.
PAP has been at the centre of current debates about free will and moral responsibility. Harry Frankfurt, an accomplished philosopher observes: “Practically no one, however, seems inclined to deny or even to question that the principle of alternate possibilities (construed in some way or other) is true. It has generally seemed so overwhelmingly plausible that some philosophers have even characterized it as an a priori truth. (p. 1).
B. PAP Argument Against Determinism (Predestination)
Critics against predestination (as a form of causal determinism) contend that (1) causal determinism rules out free will or our ability to do otherwise. Then, they conclude via (PAP) that (2) causal determinism is inconsistent with moral responsibility.
Argument Part 1
1. If someone has free will, then he is able to do otherwise.
2. If determinism is true, then he is no able to do otherwise.
3. Therefore, if determinism is true, he does not have free will.
Argument Part 2
P1 A person’s act is free and morally responsible if and only if that person could have done otherwise. (PAP).
P2 Predestination teaches that no one could have done otherwise than what he is predestined to do.
P3 Predestination is inconsistent with moral responsibility (given PAP).
C1: Predestination is not true.
The subtext of this argument is that predestination cannot be true since it undermines human moral responsibility by denying free will and makes God culpable for the sins of his creatures.
Continue reading “Reformed Compatibilist Freedom. Part 1. Critique of the Principle of Alternative Possibilities by Harry Frankfurt”
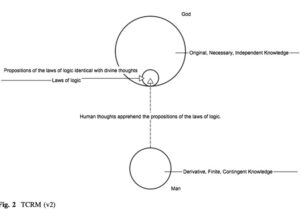
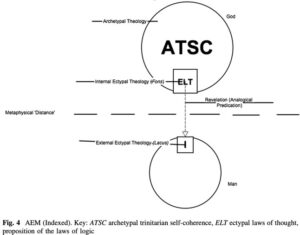




 The debate on free will has traditionally focused on how external constraints may prevent us from freely doing what we want to do. In contrast, modern psychology highlights how internal constraints (or drives) such as addictions, phobias and other kinds of compulsive behavior can be even more compelling in determining our actions. Frankfurt introduces several distinctions to our internal constraints or desires in order to shed light on they affect the way we exercise our free will.
The debate on free will has traditionally focused on how external constraints may prevent us from freely doing what we want to do. In contrast, modern psychology highlights how internal constraints (or drives) such as addictions, phobias and other kinds of compulsive behavior can be even more compelling in determining our actions. Frankfurt introduces several distinctions to our internal constraints or desires in order to shed light on they affect the way we exercise our free will.
